Birth Injury Attorneys In Phoenix
When a child is injured during the birth process, he or she may be affected for an entire lifetime. In such cases, it is important to take legal action with the help of a Phoenix birth injury attorney – not only to hold the doctor accountable for mistakes he or she made but also to help your child get the resources needed for a lifetime of care.
Helping Birth Injury Victims Seek Justice

At Harris, Powers & Cunningham PLLC, our birth injury lawyers can help. Our team of experienced attorneys has the resources, knowledge and experience to help our clients achieve the most favorable results for their birth injury cases.
Contact our office in Phoenix today and schedule a free consultation. You can reach us online or by calling 602-910-6779. If your child’s birth injury is the result of medical negligence, our lawyers never hesitate to take strong and effective legal action.
Holding Doctors Accountable For Their Mistakes
Birth injuries may result from a broad range of negligent acts by doctors and other health care providers, including:
- Not monitoring or responding to changes in fetal heart rate
- Failure to manage a delayed delivery correctly
- Mechanical problems
- Early discharge from the hospital
- Negligent use of forceps or vacuum pumps
- Overmedication
- Undetected oxygen deprivation, which can result in hypoxia-ischemic encephalopathy
- Strangulation by the umbilical cord
- Failure to manage a high-risk delivery correctly
- Failing to recognize fetal distress, which can result in cerebral palsy
- Failing to perform a cesarean section as needed
These negligent actions can lead to several serious – and often long-term – injuries and/or conditions, including cerebral palsy, shoulder dystocia, head injuries, fractures, Erb’s palsy and injuries to the spinal cord, just to name a few.
Was Your Child Diagnosed With Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy?
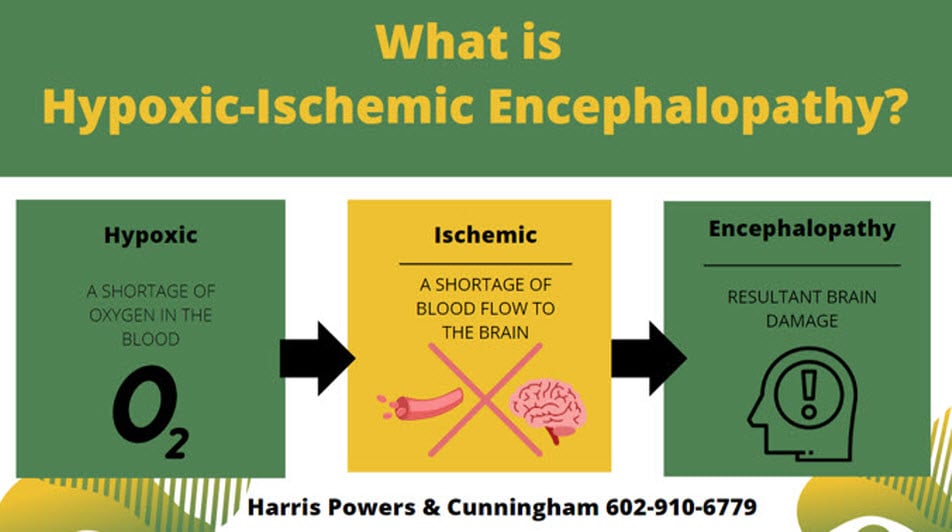
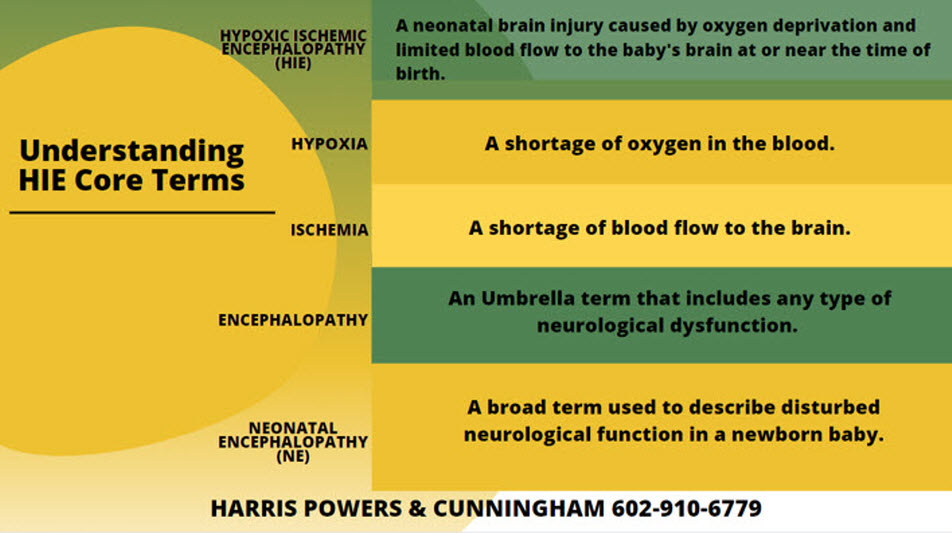
If your child has been diagnosed with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE), it may be due to a birth-related injury, and you may have a claim for legal restitution. Medical errors or negligence often cause hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE). Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy is caused by an insufficient amount of oxygenated blood flow to the baby’s brain. Hypoxic means not enough oxygen; ischemic means not enough blood flow; and encephalopathy means brain disorder. HIE is also sometimes described as birth asphyxia, perinatal asphyxia and neonatal encephalopathy. The lack of oxygen at birth can lead to severe, permanent injuries for newborns.
Causes Of Birth Asphyxia & Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE)
During pregnancy, certain conditions may make a baby more susceptible to hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE). Due to the baby’s higher susceptibility to hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE), health care providers should adjust their care accordingly. Conditions that may make babies more susceptible during pregnancy include:
- Diabetes: Diabetes and gestational diabetes, which is when a pregnant woman is diagnosed with diabetes for the first time part-way through pregnancy, may lead to an enlarged fetus, or macrosomia, which, in turn, increases the risk for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE).
- Preeclampsia: Preeclampsia is a serious condition that causes elevated blood pressure levels in the mother. These elevated blood pressure levels may affect the blood supply to the placenta, which increases the risk for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE).
- Fetal infections: Fetal infections generally occur as a result of the mother initially becoming infected by a virus before passing it to the unborn fetus, which can increase the risk of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE)if not properly managed.
- Placental insufficiency: Placental insufficiency, otherwise known as placental dysfunction or uteroplacental vascular insufficiency, is a serious complication of pregnancy. The condition is a result of the placenta failing to develop properly. This can lead to inadequate oxygen and nutrient supply to the baby from the mother’s bloodstream and can increase the risk of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE).
- Severe fetal anemia: Severe fetal anemia is the result of red blood cells and hemoglobin falling below normal levels within the fetus. Hemoglobin carries oxygen, so any restriction in the flow of hemoglobin to the fetus can increase the risk of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE).
During labor and delivery, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) may be caused by:
- Delayed delivery or cesarean section: When a baby is left in oxygen-depriving conditions because the physician spends too much time trying to deliver the baby vaginally and a C-section is delayed, the oxygen deprivation can cause hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) and other permanent brain injuries.
- Umbilical cord complications: The umbilical cord is the lifeline of the unborn. Any complications affecting the umbilical cord, such as compression or anything else that reduces its function, may put the baby at a heightened risk of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE).
- Placental abruption: Placenta abruption is a potentially serious complication during pregnancy in which the placenta becomes prematurely detached from the uterus prior to birth. The detachment can cause the unborn to become dangerously deprived of oxygen.
- Excessive use of painkillers or anesthesia: Excessive use of painkillers or anesthesia may reduce uterine activity. A decrease in uterine activity may lead to an increase in the length of labor, which may lead to hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE).
- Abnormal fetal position: Abnormal fetal positions, such as transverse fetal lie and breech, face and brow presentation, may increase the risk of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE).
- Maternal hypotension: Maternal hypotension occurs when the mother has low blood pressure. The decreased blood pressure may lead to insufficient blood flow to the baby through the placenta and umbilical cord. The reduction in blood flow may deprive the baby of oxygen-rich blood, which can lead to hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE).
After delivery, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) may be seen with:
- Severe prematurity
- Infants born prematurely have increased rates of developing hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE)
- Respiratory failure or cardiac arrest in the newborn may lead to increased chances of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) development
Signs & Symptoms Of Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE)
Signs and symptoms of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) vary greatly and are often dependent on the underlying severity and extent of the brain injury, as well as the region of the brain affected. Doctors are not likely to admit that their handling of the delivery caused your baby to develop hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE). While signs and symptoms do vary, signs of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) at birth may include the following:
- Abnormal movements or seizures
- Weakened muscles and lack of muscle tone, otherwise known as hypotonia
- Difficulty feeding, including the inability to latch, suck or swallow, due to weak muscles in the throat and mouth
- A weakened cry
- If, at birth, your baby appeared blue and required resuscitation
- Your baby seems unusually unreactive to sight and sound stimuli – for example, your baby may not react to changes in light
Additionally, a low APGAR score may suggest the newborn suffers from HIE. The APGAR test is given to newborns soon after birth, and it assesses the baby’s heart rate, muscle tone and other signs to see if extra medical care or emergency care are needed. APGAR is an acronym that stands for:
- Appearance: Is the baby abnormally pale or blue?
- Pulse: Does the baby have a normal heart rate?
- Grimace: How does the baby respond to stimuli?
- Activity: Does the baby exhibit normal joint movement and flexibility?
- Respiratory effort: Does the baby exhibit labored breathing or crying?
Diagnosing Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE)
Diagnosing hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) commonly involves the use of several tests in combination with neuroimaging. These tests usually include:
- CT scans
- PET scans
- MRIs
- Blood glucose tests
- Umbilical cord and arterial blood gas tests
- EEGs
- Ultrasounds
The results of these tests will be evaluated by a neurologist. If significant risk factors, such as fetal distress or low heart rate, occur during labor or delivery, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) may be expected, and thus, diagnostic tests should be conducted.
Newborns who suffer from hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) may not show signs of a hypoxic-ischemic injury until later in childhood. These signs commonly include delays in developmental milestones for metrics such as motor skills, growth and cognitive function.
Treatments For Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE)
While there is no definitive treatment for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE), there are treatments aimed at addressing affected organs, such as:
- Medication to control seizures
- Ventilation machines to aid in breathing
- Treatments aimed at stabilizing heart and blood pressure
- Sustaining kidney and liver function
The only brain-specific treatment that has been proven to mitigate neurodevelopmental handicaps is brain cooling.
Brain cooling, or therapeutic hypothermia, has been shown to improve a baby’s survival rate and aid in reducing the extent of permanent brain injury. By lowering the temperature of the baby’s body and brain, recovery on a cellular level may occur, as well as an increased chance of limiting the extent of future disability. The treatment involves placing the baby on a cooling blanket for three days. During this period, medical staff should provide supportive care, which may include helping the baby breathe, controlling and preventing seizures and low blood sugar and minimizing brain swelling. After three days of treatment, the baby’s body and brain will slowly be re-warmed to normal temperatures.
In addition to brain cooling, other treatments include:
- Supporting the heart and maintaining healthy blood pressure
- Sustaining kidney and liver function
- Mechanical ventilation (breathing tube) if the baby is unable to breathe independently
- Medications for babies who have seizures
Legal Help For Children With Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE)
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) cases are legally and medically complex. Though some injuries occur without fault, the unfortunate reality is that many of these incidents are avoidable and are caused by the negligence of medical staff. Due to their legal and medical complexity, you must have an attorney and law firm who are well-versed in the intricacies of birth injury and hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) litigation. Our birth injury attorneys have a litany of experience in birth injury law and are committed to securing just restitution for our clients. We focus on medical malpractice lawsuits and will offer compassion and expertise throughout the legal process.
Phoenix Cerebral Palsy Lawyers
A birth injury is an injury that a mother or baby sustains before, during or immediately following the birthing process. A birth injury is a tragic event that marks what should have been a joyous day. When a birth injury is caused by a physician’s negligence, parents are often wondering how such a mistake ever occurred.
Cerebral palsy is a brain injury that is caused by a lack of oxygen to the fetus. It is a serious birth injury that affects different children in different ways. If your baby sustained a brain injury resulting in cerebral palsy, talk to one of our Phoenix cerebral palsy attorneys today. We have won tens of millions of dollars in courtroom verdicts and settlements on behalf of our clients. We continue to succeed in securing the compensation a child with cerebral palsy will require to live as full a life as possible.
Cerebral Hypoxia And Cerebral Palsy
Cerebral hypoxia is a medical condition where the brain is deprived of oxygen. When it happens during pregnancy or during labor and delivery, it can result in mild to severe brain damage, including cerebral palsy. Hypoxia is preventable by proper monitoring of the fetus, recognition of fetal distress and timely performance of a cesarean section. Failure to perform a timely cesarean section can result in oxygen deprivation and cerebral palsy.
Cerebral palsy affects each child differently. Some parents may notice problems immediately at birth, and other effects can take a few years to surface. Children with cerebral palsy experience difficulties controlling and coordinating their muscles. Babies may have developmental delays, and the injury can severely limit the child’s quality of life and future opportunities.
Our attorneys understand the concerns of parents who are dealing with a birth injury. We provide attentive, resourceful and effective advocacy. Turn to us for help and feel confident in our abilities and our desire to help your child.
Phoenix Delayed Delivery Attorneys
A long labor and delivery can have a negative impact on the health of a child, especially when doctors fail to make the right medical decisions. When labor and delivery go on for too long, it can lead to fetal distress and brain injury. Many factors can be involved:
- Delay in performing a cesarean section (C-section)
- Incorrect use of forceps or vacuum extractors
- Misuse of labor-inducing drugs
- Failure to monitor the baby during labor and delivery
- Failure to identify breech positioning
A medical malpractice claim related to a delayed delivery injury can be complicated. That is why it is important to only work with experienced attorneys. Our experience has been developed over a 25-year history. We regularly consult with highly regarded medical experts and doctors and do legal research and investigation – all with the goal of achieving the best possible results.
Erb’s Palsy Is a Devastating Birth Injury
Erb’s palsy is the most common form of brachial plexus injury. Through the media, most people have heard the phrase brachial plexus injury but do not have a clear idea of what it actually is. The brachial plexus is a network of nerves that transmits impulses from the spinal cord to the arms and hands. An injury to this bundle of nerves can cause partial or total paralysis.
Most brachial plexus injuries occur at birth. Due to the stress placed on the body during childbirth and the lack of musculature, many babies are at risk of suffering damage to this network of nerves. Damage can result in limited mobility or feeling in the shoulders, arms and hands. While a certain percentage of brachial plexus injuries heal naturally, the rest can require physical therapy or surgery to repair the damage.
It is wise to consult with an experienced injury lawyer who can answer your questions and provide the representation you need. Through the history of our practice, our lawyers have gained insight into how to develop effective case strategies for even the most complex birth injury cases. We have extensive experience guiding clients through the process of recovering monetary compensation through personal injury lawsuits.
Phoenix Forceps And Vacuum Extraction Attorneys
A significant number of babies who experience difficult deliveries that involve the use of delivery tools like forceps and vacuum extraction experience brain injuries and other permanent impairments. Here is what to know:
- Forceps birth injuries: Forceps – large clamps that are used to turn the baby in a proper direction during delivery – can be negligently used by doctors who use them incorrectly or without enough experience. Forceps often cause injury when they are placed on the wrong part of the baby’s head. They may also be used at the wrong stage of labor. And the birth injuries this misuse causes can be serious. Babies may experience skull fractures, brain injuries, fractures, internal bleeding and blood loss.
- Vacuum birth injuries: Vacuum extractors use a soft plastic cap to suction the baby during each contraction, but they are known for causing a wide range of problems when used incorrectly. These include severe swelling of the scalp and subgaleal hematoma – bleeding between the skull and the scalp – that can lead to permanent brain damage and death.
Our Phoenix forceps extraction attorney and vacuum injury lawyers hold doctors accountable for improper use of forceps or vacuum extraction techniques by taking legal action. Our reputation can be attributed to our compassion for clients and our dedication to the pursuit of excellence in forceps and vacuum injury cases.
Phoenix High-Risk Delivery Lawyers
When a delivery is especially high-risk, the doctor should not take a delivery that is too complicated for them to handle; failure to consult with an available and more knowledgeable physician may be another form of doctor error. High-risk pregnancies and deliveries involve many factors, including:
- The mother’s small stature or pelvic anomalies
- Delayed or rapid labor
- Breech delivery
- Deliveries requiring the use of forceps or vacuum extraction
- Low birth weight
- Prematurity
- Large birth weight
- Fetal abnormalities or health problems
Doctors have a responsibility to recognize the risk factors and to take actions that prevent harm to the newborn child and the mother. When they do not do this and when harm results, they should be held accountable for their mistakes. For our high-risk delivery birth injury attorneys, this is our goal. Our Phoenix high-risk delivery lawyers have successfully represented people and their children who have experienced injury due to medical negligence in a high-risk delivery. If you or a loved one gave birth to a child who was injured during a high-risk delivery, call us today.
Why Doctors Should Recognize The Signs Of A High-Risk Delivery
Modern medicine today makes tools for fetal monitoring and diagnosis widely available. Obstetricians should use ultrasonography (sonograms) and fetal monitoring before attempting vaginal delivery. Doctors who fail to properly conduct fetal monitoring may be committing medical malpractice.
Preterm Labor And Premature Births
Premature births are another common type of high-risk delivery. When labor starts too early, the fetus may not have developed enough to survive outside of the womb. Serious injury or death to the child may result, especially when doctors fail to diagnose and treat special conditions in preemies.
Answers To Frequently Asked Questions About Birth Injuries
Below, we’ve provided answers to common questions we are asked by prospective clients. If you have additional questions, we would be happy to provide answers during a free initial consultation.
What are examples of birth injuries?
There are many injuries that can occur during birth. Some examples of catastrophic birth injuries include:
- Cerebral palsy
- Paraplegia
- Brain damage
- Seizure disorders
Most birth injuries, however, are not life-altering. These include:
- Bruised or torn nerves in the face, resulting in partial facial paralysis (which could improve on its own or require surgery)
- Damage to the group of nerves known as the brachial plexus, resulting in a condition called brachial palsy
- Marks or bruises left by the forceps used to aid in delivery
Though these injuries by themselves are not typically catastrophic, they can be used as persuasive evidence that there was a traumatic birth process leading to your baby’s catastrophic injury of cerebral palsy, paraplegia, brain damage, seizure disorder, etc. Therefore, it is important to seek a legal opinion if you believe malpractice was a factor in your baby’s injury.
How common are birth injuries?
It is difficult to compile accurate statistics on this issue because birth injuries are underreported. However, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that approximately seven babies out of every 1,000 births will suffer a birth injury.
What are the risk factors for birth injuries?
Risk factors for birth injuries include the size of the mother and baby, how the baby “presents” in the birth canal (headfirst or breach), a mother’s development of preeclampsia around the time of birth, as well as many others. Health care providers must appropriately respond to and treat risk factors to avoid causing injury.
Can a traumatic birth injury affect the baby?
Any physical birth injury a baby experiences can have a long-term impact, both physically and psychologically.
What are the signs and symptoms of birth injuries?
The specific symptoms and signs will depend on the injury. If your baby suffers from cerebral palsy to the face or to a limb, you may notice a lack of expression, muscle spasms, lack of tone or tremors. If the baby is often lethargic or unresponsive, it could be a sign of brain injuries caused by oxygen deprivation.
Unfortunately, some symptoms, such as developmental delays, may not become apparent for months or even years after birth. If your delivery was especially difficult and you believe that your baby may have suffered a birth injury, it is important to be vigilant and consult with a physician you trust regarding any symptoms that seem more significant than ordinary health issues.
It is also important to seek legal counsel immediately if you feel your child has suffered a birth injury.
In Arizona, there is a statute of limitation for medical malpractice claims. The statute of limitations is a time limit for filing a lawsuit. For parental claims, the lawsuit must be filed with the court within two years from the date of injury or two years from when the person knew or should have known that negligence occurred. For children, the statute of limitations does not begin to take effect until their eighteenth (18th) birthday. This means your child has two years after turning eighteen to file a lawsuit to preserve their claim. Failure to comply with the applicable statute of limitation will result in the claim being barred.
How could a birth injury impact the lifetime care of a child?
Depending on the type and severity, a birth injury could greatly impact the lifetime care of a child and limit the child’s potential. Severe oxygen deprivation, for instance, could result in significant brain damage that makes it impossible for a child to eventually become a self-sufficient adult. The child may require constant care throughout their entire life, the financial costs of which can be in the millions of dollars.
Seek Help Today From A Birth Injury Attorney
Sometimes, medical care professionals fail to diagnose or properly treat conditions that arise during pregnancy, which can lead to birth injuries. When doctors fail to identify that something is going wrong, they may also be committing malpractice.
Take the first step in determining whether or not you have a medical malpractice claim related to a birth injury in Arizona. Call us at 602-910-6779 or contact one of our attorneys online today for help.


